ATTR is a progressive and fatal disease1
Starting treatment at diagnosis is key to delaying disease progression2
ATTR is a multisystem disease caused by pathogenic TTR3-6
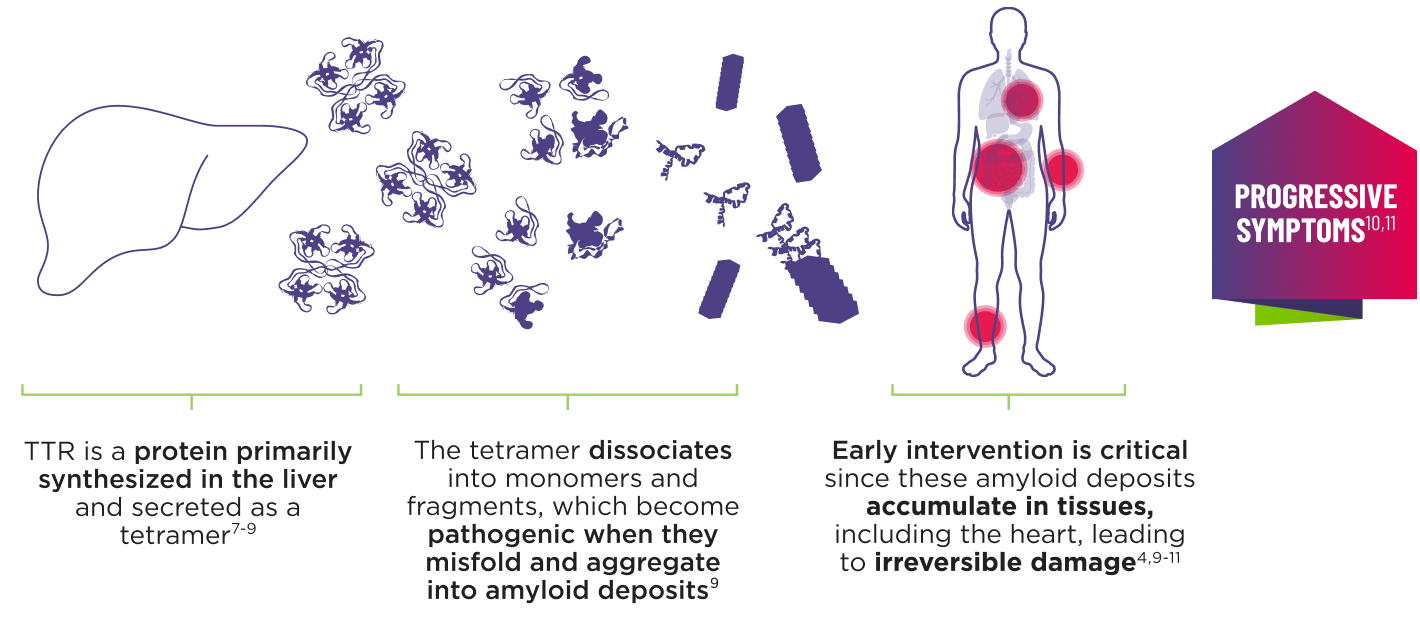

Cardiomyopathy is a common manifestation of ATTR (ATTR-CM) that may lead to heart failure; musculoskeletal manifestations, polyneuropathy, and other symptoms may also present.4,6,12
- Transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTR) is an underdiagnosed, progressive, debilitating, and fatal disease1
- Patients with ATTR may be diagnosed 3 to 8 years after symptom onset1,13,14
- If left untreated, the median survival for patients with ATTR is 2.5 to 5.5 years post-diagnosis15-18
There are 2 types of ATTR

wtATTR is related to aging and typically manifests as cardiomyopathy. The etiology of wtATTR is unknown.10,19,20
hATTR is caused by a variant in the TTR gene and can manifest as cardiomyopathy or polyneuropathy. Mixed phenotype is the most common presentation.10,19,20
Either type of ATTR can have a heterogeneous symptom presentation.10
ATTR is a multisystem disease10
The presence of these red-flag symptoms may help identify patients with ATTR
Cardiac
Elevated NT-proBNP, unexplained left ventricular wall thickening in the absence of hypertension, conduction system disease/atrial fibrillation, HFpEF in combination with other noncardiac red-flag symptoms21-26
Sensory-motor neuropathy
Length-dependent neuropathic pain and weakness, altered sensation, difficulty walking2
Gastrointestinal manifestations
Diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, unintentional weight loss2
Musculoskeletal
History of musculoskeletal symptoms (eg, carpal tunnel syndrome, lumbar spinal stenosis, or biceps tendon rupture), past orthopedic surgery21,23
Autonomic neuropathy
Orthostatic hypotension, recurrent urinary tract infections, sexual dysfunction, sweating abnormalities, urinary retention2
AMVUTTRA does not treat all of the symptoms of ATTR. AMVUTTRA is approved to treat ATTR-CM and hATTR-PN in adults.
ATTR-CM=cardiomyopathy of transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; hATTR-PN=polyneuropathy of hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; HFpEF=heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; NT‑proBNP=N-terminal prohormone of brain-type natriuretic peptide.
